¶ Parts of Speech
NOUN:
A noun is the name of a person, place, thing, or idea.
Based on what kind of -person, place, thing, or idea a noun represents, nouns can be classified into 5
types.
1. Common noun- People, Books
2. Proper noun - Sara, The Great Gatsby
3. Concrete noun- Building, Coffee
4. Abstract noun- Love, Truth
5. Collective noun- Team, Family
Based on the ‘number’ of the -person, people, place, or idea that a noun represents, nouns can be
classified into 2 types.
1. Countable (Count nouns)
2. Uncountable (Non-count nouns)
PRONOUN:
Pronouns have a very close association with nouns. They are basically words that replace nouns in a
sentence. These words are introduced in a sentence to avoid repetition of the same nouns. Whenever
used, a pronoun must have a referent noun which we call ‘antecedent’. To put it very simply, the noun
which is replaced by the pronoun from the sentence is called ‘antecedent’ of that pronoun.
**The antecedent and the pronoun have to be in the same person and number.
The girls were very happy. It must have heard the good news.
The girls were very happy. They must have heard the good news.
**There must be one, and only one antecedent to which the pronoun refers.
The girls were happy to see their parents. They were very excited to see them indeed.
The girls were happy to see their parents. The parents were very excited to see their children indeed.
Pronouns are primarily classified into 8 categories. They are-
1. Personal Pronoun- I, Me, Us
2. Possessive Pronoun- My, your
3. Reflexive Pronoun- myself, yourself
4. Reciprocal Pronoun- each other, one another
5. Relative Pronoun- that, which, who
6. Demonstrative Pronoun- this, that, these, those
7. Interrogative Pronoun- what, who, whom
8. Indefinite Pronoun- anyone, everyone, some
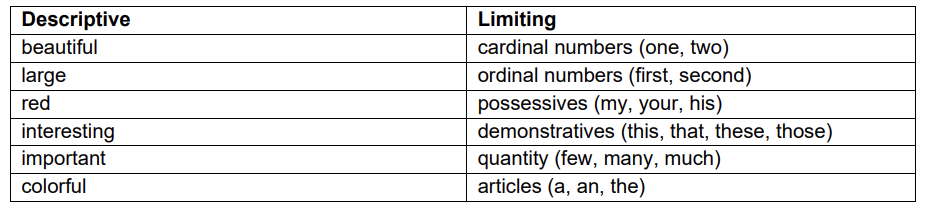
ADJECTIVE:
Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns.
The answers to the following question are generally adjectives: What kind?, Which one?, How many?, How much?
VERB:
Verbs are technically action words. However, they can describe an occurrence or a state of being as well.
ADVERB:
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. They modify in that they answer the following
questions in relationship to the nouns they modify,
• When?
Arrive when? Tomorrow.
• Where?
Dance where? Everywhere.
• How often?
• Dance how often? Frequently.
• How much?
costs how much? a lot.
PREPOSITION:
Prepositions are words or set of words those indicate location (in, near, beside, on top of) or some other
relationship between a noun or pronoun and other parts of the sentence within the sentence (about, after,
besides, instead of, in accordance with).
CONJUNCTION:
Conjunctions are words those link other words, phrases, or clauses together.
Coordinating Conjunctions
for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so
Correlative Conjunctions
both/and, either/or, neither/nor, not only/but, whether/or
Subordinating Conjunctions
after, although, as, as if, as long as, as much as, as soon as, as though, because, before, by the time, even
if, even though, if, in order that, in case, in the event that, lest , now that, once, only, only if, provided that,
since, so, supposing, that, than, though, till, unless, until, when, whenever, where, whereas, wherever,
whether or not, while
INTERJECTION:
Interjections are parts of speech those demonstrate the emotion or feeling of the author.
Eww - Something disgusting
Eww! That movie was so gory.
Hmph - To indicate displeasure
Hmph, I could do that for half the amount he did.
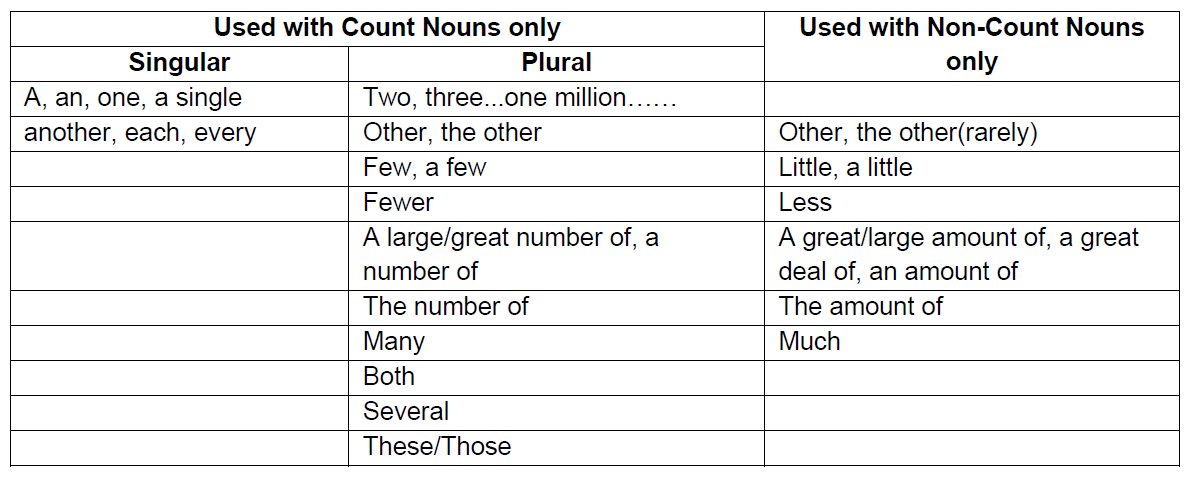
Countable Noun
Countable nouns refer to something that can be counted. Example: TV, phone, shoe, country.
Sentence: Telephones are redundant, mobile phones are the new hype.
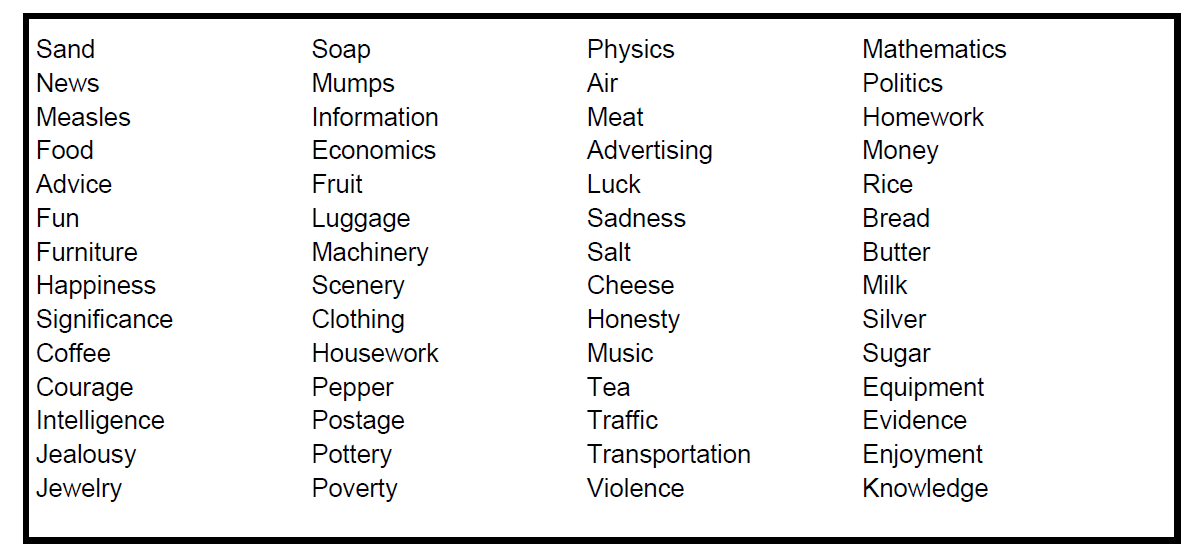
Uncountable Noun/ Non-count Noun:
Uncountable nouns refer to things that can not be counted. Example: happiness, air, rice, Hair.
Sentence: Love is in the air.

A list of some non-count nouns that one should have knowledge about
WARNING:
- Non-Count Nouns always take singular verbs.
- We cannot use adjectives like “a,” “one/two/three,” “another,” etc to modify Non-Count Nouns.
soap/ a bar of soap ( not a soap ×)
information/news/furniture or a piece of information/news/furniture (not a news × )
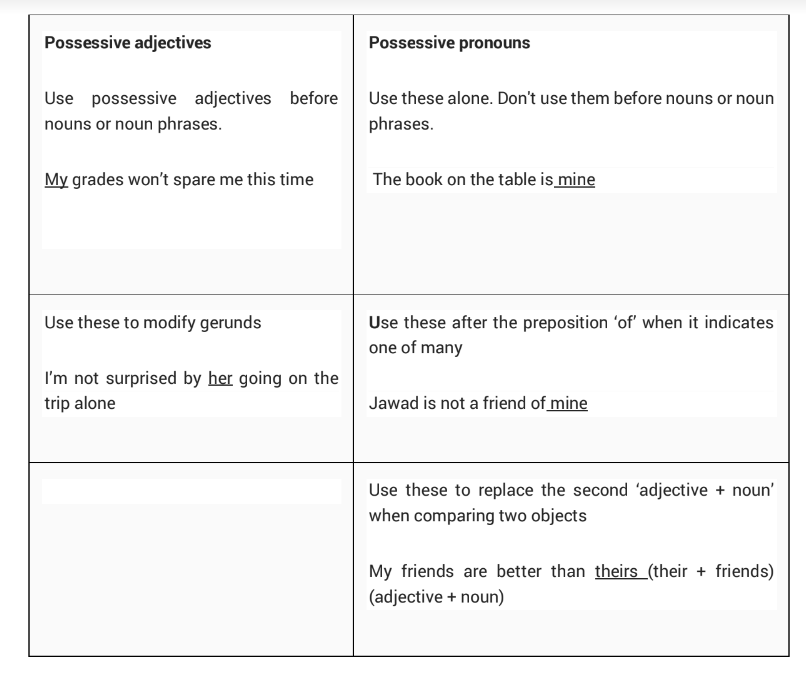
Possessive Adjectives vs Possessive Pronouns
Reciprocal Pronouns
Reciprocal pronouns are similar to reflexive pronouns, but they involve groups of two or more entities
that perform the same action with one another.
There are only two reciprocal pronouns:
each other (for groups of two), and one another (for larger groups).